Table of Contents
Introduction
Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals. it constitutes +/-30% of all protein in the human body.
We refer to collagen in its natural state as native collagen, this is the collagen fibre bundles as it is found in the body.
Dietary collagen, digestive collagen or collagen powder as most brands refer to their products are in fact not native collagen but hydrolyzed collagen. Hydrolyzed collagen should be referred to as “hydrolysed collagen” or “collagen peptides” as required by law.
Most collagen powders on the market are incorrectly labelled and are therefore misleading to the consumer.
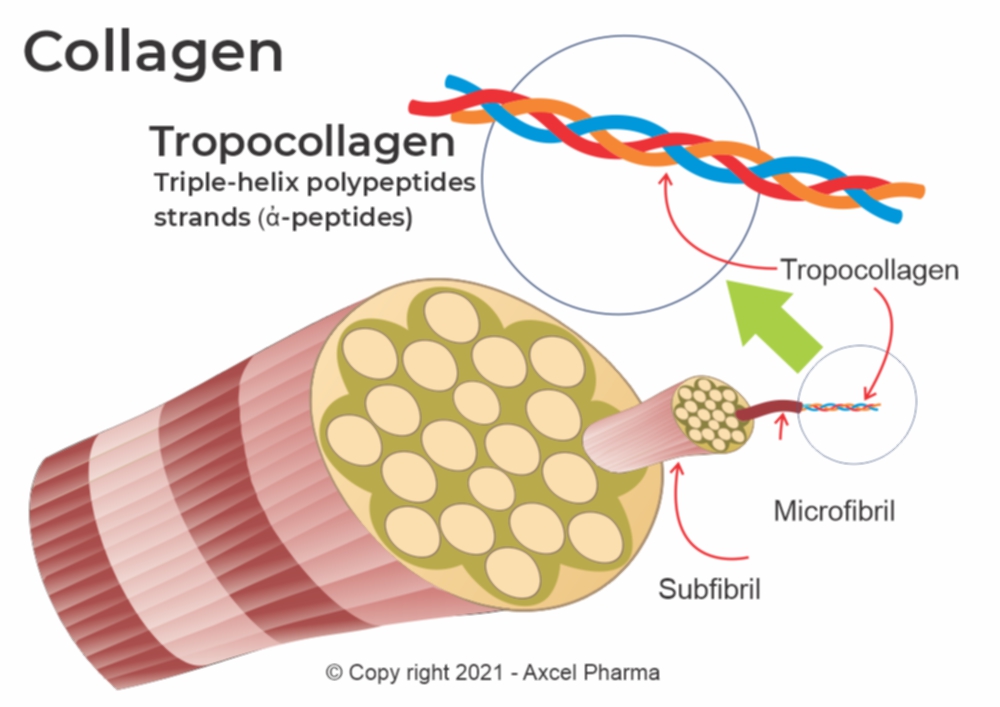
What is Native Collagen?
Collagen or native collagen consists of fibrous strands called fibrils packed in bundles called collagen fibres. The fibrils in turn are made up of subfibrils and microfibrils.
These consist of Tropocollagen, the structural unit of collagen fibre. It is made up of three polypeptide strands (referred to as alpha peptides) that are twisted together into a superhelix or a right-handed triple helix.
These fibres are insoluble and can’t be digested or absorbed by the human digestive system.
The Tropocollagen triple helix structure has to be treated with a process called “hydrolysis” whereby water (hydro) is heated to a specific temperature to denature the collagen so that the alpha-chains are separated into single ἀ-chains.
Very specific enzymes are added to cleave the chains at specific links to form di- and tri-peptides with a low molecular weight of between 300 and 2000 Da (Dalton).
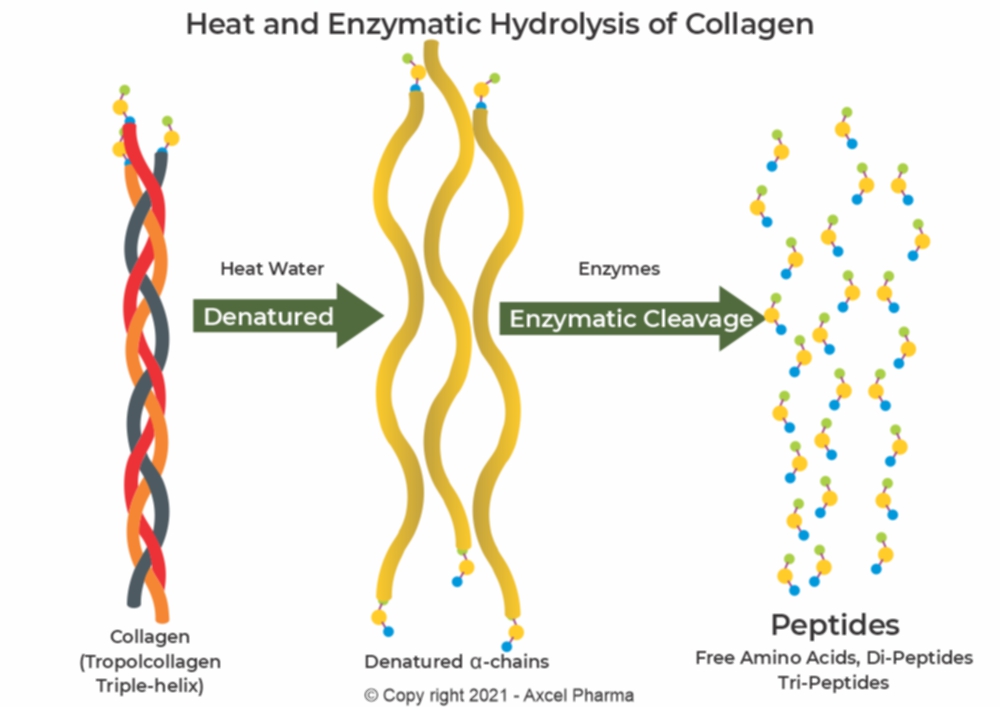
What are Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides
Hydrolyzed collagen consists of small peptides with low molecular weight (0.3 – 2 kDa), produced from native collagen found in bones, skin and connective tissue of animals (i.e. cattle and fish). Due to its low molecular weight, hydrolyzed collagen is easily digestible, absorbed and distributed in the human body.
The final hydrolyzed collagen’s quality depends on its average molecular size, which can vary based on the methodology used to extract it. Generally, collagen molecules are denatured and partially hydrolyzed to form gelatin (100 kDa). Gelatin can then be enzymatically digested into small peptides using specific enzymes with cleavage activity (proteinase).
(Fig. (2)). The molecular weight distribution of collagen peptides usually spans in the range 0.3 – 2 kDa. Due to the low molecular weight, there are several advantages of using hydrolyzed collagen with respect to native collagen:
- hydrolyzed collagen is highly digestible,
- hydrolyzed collagen is highly bio-available,
- hydrolyzed collagen is easily absorbed and distributed in the human body.
Watch this Video
Also, read these articles:
- What is Collagen?
- Skin Health
- Bone Health
- Joint Health
- Connective Tissue Health
- Collagen benefits for Hair